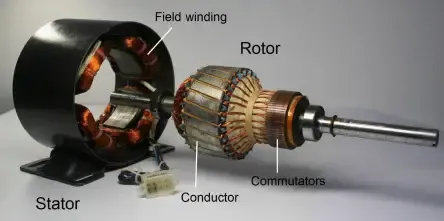
DC series motors and Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) motors differ primarily in their construction and performance characteristics. DC series motors have field windings connected in series with the armature, resulting in high starting torque and variable magnetic field strength based on current. They are ideal for applications requiring strong initial torque but are less efficient and more complex to control. In contrast, PMDC motors use permanent magnets to generate a constant magnetic field, making them simpler, more efficient, and easier to control, see for example tutorial Joystick controlled DC motor with Arduino and TIP122. PMDC motors are commonly used in smaller, consistent load applications, such as RC cars see example tutorial Controlling Motor Speed with PWM Arduino, where efficiency and simplicity are prioritized.
1. Construction:
DC Series Motors:
- The field windings (stator) and the armature (rotor) are connected in series.
- The magnetic field is generated by the current flowing through both the armature and field windings.
- Typically larger and more complex compared to PMDC motors due to the additional windings.
PMDC Motors:
- The stator consists of permanent magnets instead of windings.
- The magnetic field is generated by these permanent magnets, so no additional power is needed for the field.
- Simpler construction, often more compact and lightweight.
2. Magnetic Field:
- DC Series Motors:
- The magnetic field strength depends on the current through the windings. As the load increases, the current increases, strengthening the magnetic field.
- PMDC Motors:
- The magnetic field is constant, provided by the permanent magnets, and does not depend on the current through the motor.
3. Torque-Speed Characteristics:
DC Series Motors:
- High starting torque, which decreases as speed increases.
- Ideal for applications needing strong initial torque, such as RC cars or electric traction.
PMDC Motors:
- Provides a more consistent torque across various speeds.
- Less variation in torque compared to series motors, making them better suited for applications where steady performance is needed.
4. Efficiency:
DC Series Motors:
- Generally less efficient due to power losses in the field windings.
- Larger and heavier, which can lead to greater energy consumption.
PMDC Motors:
- More efficient since they don't require energy for generating the magnetic field.
- Typically lighter and more power-efficient for the same output.
5. Control:
DC Series Motors:
- More complex to control because the speed and torque are more closely linked to the current.
Resources
Brushed DC motor vs Out-runner BLDC motor structural comparison